USB Power Delivery
<What is USB Power Delivery?>
What is USB Power Delivery?
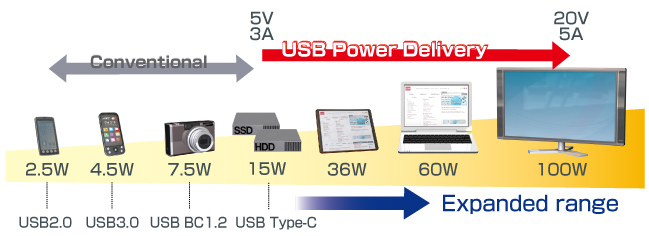
USB Power Delivery (USB PD) is a USB power extension standard that allows up to 100W to be received using the new Type-C USB cable.
Previous standards included the USB2.0, that stipulates up to 2.5W, USB3.0, which maxes out at 4.5W, and USB BC1.2 (Battery Charging) that supplies up to 7.5W for battery-equipped devices.
The extended power range up to 100W stipulated by USB Power Delivery supports devices such as laptops and tablets that were not possible with previous standards, significantly expanding the applicable range.
Rapid charging (shorter charging time) of mobile devices is also possible.
USB Power Delivery Application Examples
USB Type-C
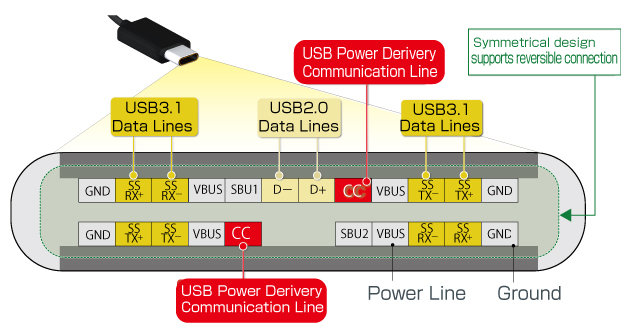
USB Power Derivery specifies the connector cable to be used for power supply.
The new USB Type-C connector has been established and promoted by USB Implementers Forum, Inc. (USB-IF), an organization that promotes the standardization and management of USB specifications.
In contrast with conventional USB, which utilizes a Type-A connector on the Host side and Type-B on the device side, Type-C stipulates the same connector on both sides, eliminating the need to differentiate connector types.
Also, unlike the Type-B connector that comes in a variety of different shapes in addition to the standard type, including Mini-B and Micro-B (making it necessary to configure the connector type based on device), Type-C specifies one shape for all applications, achieving a common standard.
In addition, since there is not up or down orientation, the connector can be inserted in either direction.
And video signals are supported, enabling data, power, and video signal transmission using a single USB cable.
Communication necessary for USB PD is performed on the dedicated CC line, allowing it to function independently of conventional USB operation.
USB Type-C Pinout Diagram