Zener Diode (ZD)
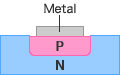
Structure and Features
| Structure | Symbol | Applications・Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|
Zener diodes are typically used in constant voltage circuits to ensure constant voltage even if the current fluctuates or as protection elements against surge currents and ESD. The input voltage, which should exceed the Zener voltage in relevant circuits, plays a crucial role in maintaining a constant output voltage despite variations. Unlike standard diodes that are employed in the forward direction, Zener diodes are designed to be used in the reverse direction. The reverse breakdown voltage of a Zener diode is referred to as the Zener voltage VZ, and the current value at this time is called the Zener current (IZ). The reverse bias voltage allows the diode to conduct significantly, and as the reverse voltage increases, the reverse current flows drastically, reaching the Zener voltage. In recent years, with the continuing miniaturization and increasing performance of electronic devices comes a need for more advanced protection devices, bringing about the emergence of TVS (Transient Voltage Suppression) diodes. Zener diodes help achieve a stable output voltage that is less affected by variations in load current.
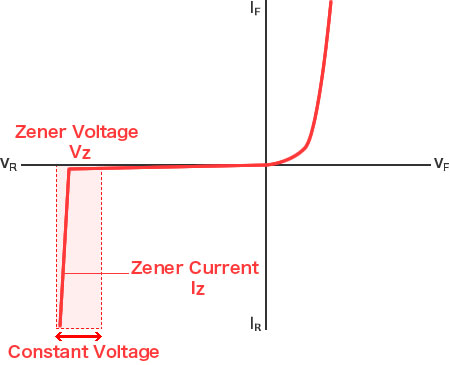
Zener diodes effectively regulate voltage drop in reverse-bias mode, maintaining a constant voltage output despite fluctuations in input voltage or load conditions. The Zener breakdown voltage is the specific reverse bias voltage at which the diode begins to conduct significantly, ensuring stable operation.
When the Zener diode exceeds its specified breakdown voltage, it begins to conduct in reverse bias, stabilizing and maintaining a constant voltage across the load. Zener diode specifications, such as power dissipation, nominal working voltage, and maximum reverse current, are essential for selecting the appropriate Zener diode for specific applications.
Zener diodes are widely used in voltage regulation applications, functioning as a zener voltage regulator to maintain a constant output voltage across loads despite fluctuations in input voltage. They are designed to operate in reverse and maintain a wide range of Zener voltages for effective voltage regulation.
Key Points on Zener Diodes
- A decoupling capacitor can be added to the output of the Zener diode to help mitigate electrical noise generated on the DC supply. This high-value capacitor provides additional smoothing for the voltage, ensuring a more stable performance in voltage regulator circuits.