Types of Operational Amplifier
Dual Supply / Single Supply / Rail-to-Rail Op Amps
Op amps can be classified into 3 main types based on the input/output voltage range: Dual Supply, Single Supply, and Rail-to-Rail. The output signal of an op amp is the amplified signal produced, which is crucial in determining the performance and application of the op amp. Understanding the input impedance and output impedance is crucial when selecting and using different types of op amps, as these parameters significantly affect performance, power consumption, and circuit behavior. The input/output voltage range of each type of op amp is shown below.
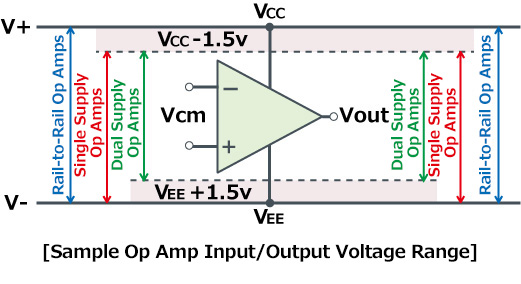
Dual Supply Op Amps (Offset Voltage)
Since op amps generally amplify small signals close to 0V, when 0V input is required, in the case of a dual supply op amp VEE must be set to -1.5V or less. For applications requiring higher accuracy, it is important to consider the input offset voltage, as it leads to an offset in the amplifier’s output voltage. For this reason, a negative power supply is often used, and since both positive and negative supplies are required, it is called a dual supply op amp.
An ideal dual supply op amp should have zero output impedance to ensure it can supply full current to the load connected to the output.
Negative feedback is crucial in dual supply op amps as it stabilizes the gain and reduces output impedance, ensuring accurate performance and stability.
> Low Noise Power Supply Op Amps (Product Search)
> Low Offset Dual Supply Op Amps (Product Search)
Single Supply Op Amps (Ground Sense)
When inputting signals near 0V, a negative voltage is needed if using a dual supply op amp (general purpose), but an op amp that enables input without this negative voltage is called a single supply op amp. Single supply op amps have high input impedance between the negative and positive input terminals, which is crucial for various configurations such as voltage amplifiers and voltage followers.
In an inverting amplifier configuration, the input signal is applied to the inverting input, and the output signal is 180 degrees out of phase with the input signal.
It is also referred to as a ground sense op amp since it can operate up to the ground level input signal. The inverting input plays a significant role in different circuit configurations, including inverting amplifiers, non-inverting amplifiers, and closed-loop amplifiers, by determining the gain and feedback characteristics.
> General Purpose Ground Sense Op Amps (Product Search)
> High-Speed Ground Sense Op Amps (Product Search)
> Low Current Ground Sense Op Amps (Product Search)
> Low Noise Ground Sense Op Amps (Product Search)
> High-Performance Ground Sense Op Amps (Product Search)
Rail-to-Rail Op Amps (Input Voltage/Output Full Swing)
With the recent trend towards energy conservation, a greater number of sets are being driven at low voltages. A differential amplifier is a type of operational amplifier that converts a differential signal at the input into a single-ended signal at the output, making it essential for applications requiring precise voltage amplification. Closed-loop gain is crucial in rail-to-rail op amps as it ensures stable circuit behavior across various factors like temperature, process shifts, and voltage changes by using negative feedback through external components. Op amps also need to operate at low voltages, but if the VCC drops to nearly 5V, a single supply op amp is able to only input 1.5V less than VCC, which can be inconvenient. In contrast, a Rail-to-Rail op amp can operate normally even when the input voltage swings from VEE to VCC. External resistors play a significant role in determining the characteristics of rail-to-rail op amps through negative feedback. The voltage follower is a basic operational amplifier circuit that provides high input impedance and low output impedance, functioning as a useful buffer where changes to the input produce equivalent changes to the output voltage. Because it can input/output over the full supply voltage range (VEE to VCC), it is often called an input/output full swing op amp.
> High Speed Input/Output Full Swing Op Amps (Product Search)
> Low Current Consumption Input/Output Full Swing Op Amps (Product Search)
> Low Noise Output Full Swing Op Amps (Product Search)
> Low Offset Input/Output Full Swing Op Amps (Product Search)
For application circuit examples of various types of op amps, please refer to the application notes using the link below.
> Op Amp Application Circuit Examples (Application Notes)
The next page defines noise characteristics, which is a major issue with op amps.




