IPDs
What is an IPD?
An IPD, or
Intelligent
Power
Device, is a high performance semiconductor power switch with built-in
protection circuits capable of absorbing energy such as inductive
loads.
Depending on the region, it may also be called an IPS (Intelligent
Power Switch), Smart Switch, or High Side/Low Side Switch.
IPD Feature 1 (Comparison vs MOSFET)
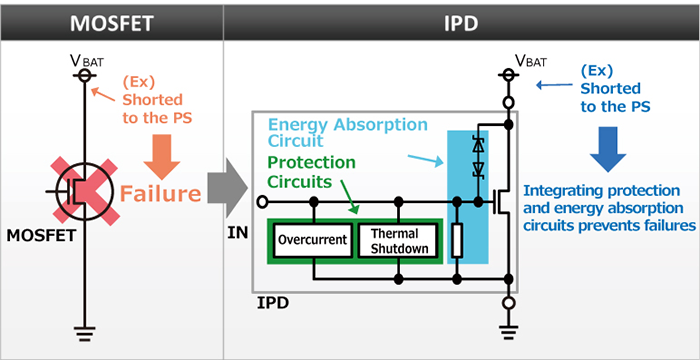
Typically, MOSFETs are the first components that come to mind when
thinking about semiconductor switches.
However, when using a single MOSFET as a switch, the MOSFET itself may
fail if the load shorts on the mounted circuit.
In contrast, IPDs incorporate circuits that protect against excessive
current and heat as well as for absorbing energy (i.e. from inductive
loads), allowing them to maintain switch functionality without
breaking down due to abnormal conditions such as short-circuits.
[IPD vs MOSFET]
IPD Feature 2 (Comparison vs Fuse)
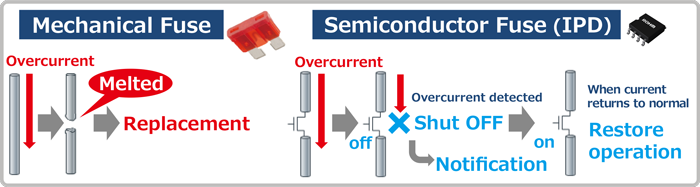
Fuses are components that prevent excessive current flow.
Mechanical fuses stop current flow by opening the circuit during
overcurrent conditions. However, they must be replaced in order to
resume normal operation.
Conversely, using an IPD as a semiconductor fuse makes it possible to
detect abnormalities such as overcurrent and stop current flow. A
notification function (i.e. to the MCU) is also built in that can be
effective in analyzing the root cause. What's more, IPDs are
self-restoring, therefore no replacement is needed.
[IPD vs Mechanical Fuse]
IPD Feature 3 (Comparison vs Mechanical Relay)
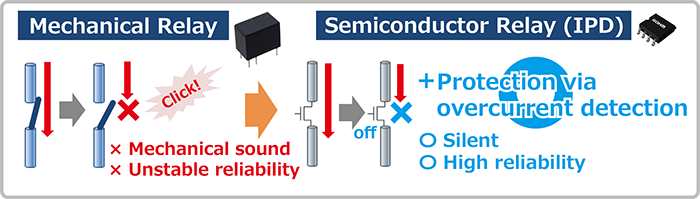
Relays are components that switch electrical circuits ON/OFF using an
external signal.
As mechanical relays have mechanical contacts, there are concerns
regarding service life and reliability. In addition, relays typically
generate a mechanical sound when switching.
Semiconductor relays using IPDs, on the other hand, feature no
mechanical contacts, resulting in longer life, higher reliability, and
quieter operation. Also, their compact lightweight form factor
supports reflow soldering, and they provide not only relay
functionality for switching ON/OFF, but protection as well by
detecting overcurrent.
[Comparison vs Mechanical Relay]




