Chip Resistor Specifications
Chip Resistor Sizes
The external dimensions of chip resistors are typically designated using company-specific notation and are indicated in both mm and inches.
| ROHM Part No. | Chip Size (Length x Width) |
mm | inch |
|---|---|---|---|
| ***004 | 0.4 mm × 0.2 mm | 0402 | 01005 |
| ***006 | 0.6 mm × 0.3 mm | 0603 | 0201 |
| ***01 | 1.0 mm × 0.5 mm | 1005 | 0402 |
| ***03 | 1.6 mm × 0.8 mm | 1608 | 0603 |
| ***10 | 2.0 mm × 1.2 mm | 2012 | 0805 |
| ***18 | 3.2 mm × 1.6 mm | 3216 | 1206 |
| ***25 | 3.2 mm × 2.5 mm | 3225 | 1210 |
| ***50 | 5.0 mm × 2.5 mm | 5025 | 2010 |
| ***100 | 6.4 mm × 3.2 mm | 6432 | 2512 |
***Represents part numbers (excluding chip networks)
What is 'Rated Power'?
Rated power and ambient temperature
Rated power is the maximum power that can be used in continuous operation at the rated ambient temperature.
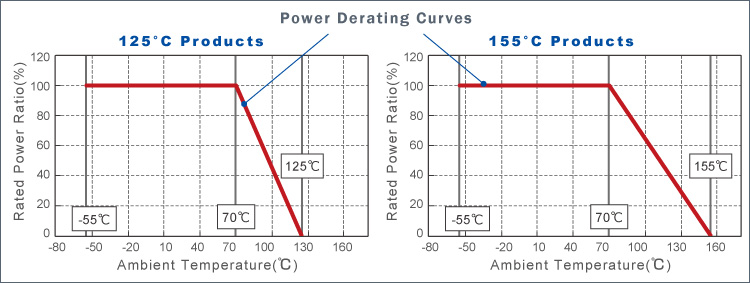
Chip resistors generate heat when power is applied.And since the upper limit of the operating temperature is fixed,power derating must be carried out according to the following power derating curve when used at the rated ambient temperature or higher.
Rated ambient temperature is the maximum temperature at which 100% of the rated power can be applied.
In the figure below, the rated ambient temperature is 70°C. Please note that this temperature will vary depending on the type of chip resistor.
Ambient temperature mentioned here refers to the temperature surrounding the resistor at room (atmospheric) temperature or heat generated around the resistor when the resistor itself is not electrically loaded.
The JIS standard defines the ambient temperature at the place where there is no effect of heat generation by the resistor itself.
However, if it is difficult to measure the ambient temperature under the actual usage environment,
an alternative is to measure the substrate temperature near the product or the air temperature 1cm above
(although these conditions are stricter than the JIS standard).
Details on the JIS standard can be found here :https://www.rohm.com//products/faq-search/faqId/290
Rated power when the rated ambient temperature is exceeded
If the rated ambient temperature is exceeded, the permissible power decreases according to the derating curve.
In other words, it is necessary to reduce the permissible power based on the power derating curve in environments where the rated ambient temperature may be exceeded.
Let’s take a look at the following example.
[Ex]
・ In the case of a rated ambient temperature of 70°C and an operating temperature of 130°C:
There are two ways to verify the ratio of applied power - one is to confirm from a graph and the other is to calculate using a formula.To determine from a graph, use the following procedure.
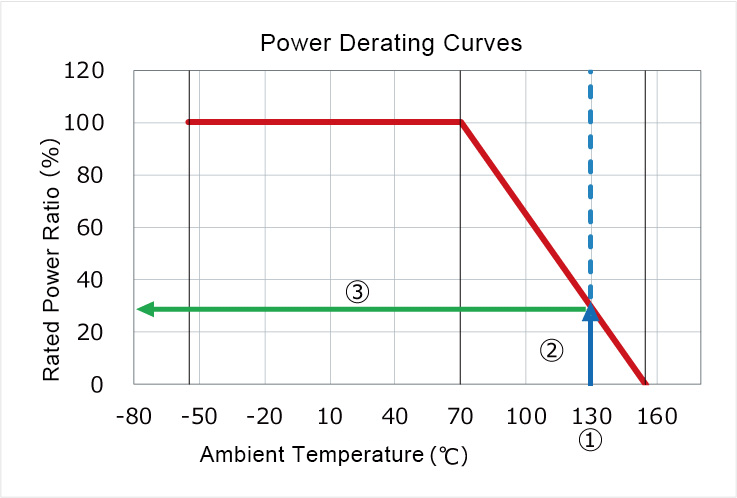
- ① On the horizontal axis find the ambient temperature of 130°C
- ② Draw a vertical straight line such that x=130°C
(Blue Line) - ③ Read the value where the blue line intersects the derating curve by drawing a horizontal line(red)
(Green line:Power ratio where the value read can be applied)
Alternatively, the derated power can be calculated using the following formula.
![Ratio of rated power that can be applied for a given ambient temperature[%]](/documents/11303/9970704/what_8_03.gif/acb2d2b3-af09-e411-fabb-5def1c0b4845?t=1645078911906)
Applying this formula to our example, we get
![Ratio of rated power that can be applied at an ambient temperature of 130°C[%]](/documents/11303/9970704/what_8_04.gif/0bcda570-faf3-8e8e-dacb-9874c673973b?t=1645078911232)
Referencing the above, please use after reducing the power to the rated power ratio determined from either method.
Regardless of the ambient temperature, it is necessary to check the rated voltage separately when using resistors.
Since the rated voltage is calculated from the rated power and resistance value,
please calculate it from the rated power after derating.
Standard Chip ResistorsDownload datasheet
The next page gives a brief description of the rated voltage and other voltage considerations.




