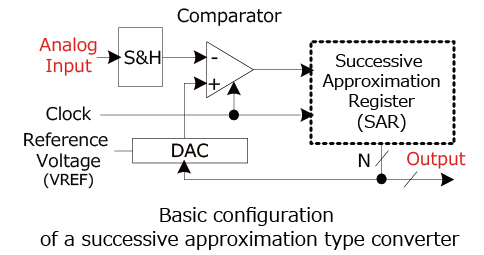
ADC Basic Configurations 3 (Approximation Method)
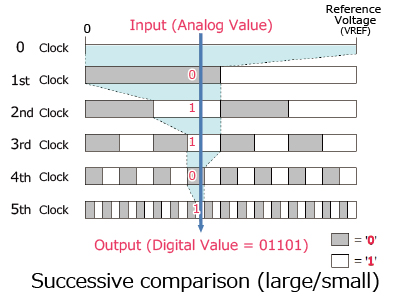
This method compares the sampled analog input with the converter's output in succession, starting with the MSB.
- The analog input signal is sampled (S&H)
- A successive approximation register (SAR), which is designed to supply an approximate digital code to the internal DAC, is initialized so that the most significant bit (MSB) is set to '1'.
- The digital values from the SAR are converted into equivalent analog values by the internal DAC.
- The sampled input voltage is compared with the DAC output voltage.
- If the sampled voltage > DAC output voltage → MSB = 1
- If the sampled voltage < DAC output voltage → MSB = 0
The digital conversion is completed by repeating the operation up to LSB.
Characteristics:
- High resolution conversion possible (up to 18bit)
- Since a clock cycle is required (resolution + α), conversion speed is moderate (10MHz max. sampling frequency)
- Good response. Connecting a multiplexer to the the input makes it easy to switch analog signals.




