ADC Basic Configurations 4 (ΔΣ Method)
After oversampling of an analog signal is performed and converted into low-bit data (i.e. 1bit) corresponding to the amplitude of the analog signal using ΔΣ modulation, the analog to digital converter completes the conversion into a digital signal at the original sampling rate by removing out-of-band noise using a digital filter, resulting in a precise digital output.
Oversampling in Analog to Digital Converter
Quantization error is decreased by sampling at a higher frequency than the original sampling frequency.
Oversampling helps in reducing quantization noise by spreading it across a wider frequency range, which enhances the overall performance of ADCs.
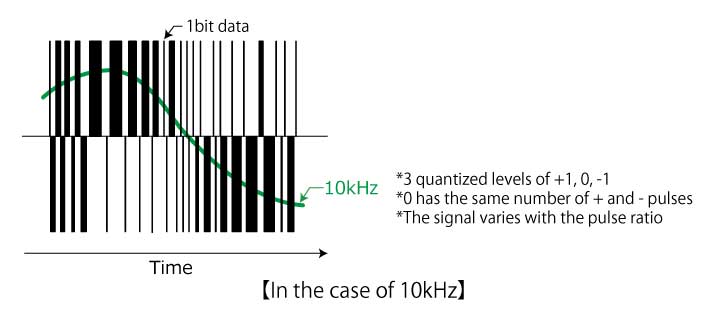
ΔΣ Modulation and Quantization Noise
The difference (Δ) between the DA converter output voltage and sampled voltage (via oversampling) is integrated (Σ) by the integrator. This integrated value is then converted to low-bit data by comparing with a reference voltage using a comparator, resulting in a digital representation.
Delaying the output data by one sampling operation and feeding it back to the input allows modulation to be carried out so that the quantization error generated by the comparator is smaller in the low frequency range and larger in the high frequency range.
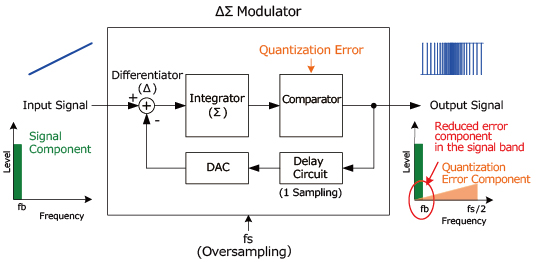
Low-bit data output from the ΔΣ modulator has a large quantization error component in the high-frequency region in addition to the original signal component. However, since these components are separated in frequency and only the quantization error component can be removed by the digital filter, high resolution not possible with other methods can be achieved. The digital value produced by the ΔΣ modulator is thus highly accurate.
Compared to other ADC types like pipelined ADCs and successive approximation register (SAR) ADCs, the ΔΣ method offers higher resolution but generally slower conversion speeds. Pipelined ADCs achieve higher sample rates and resolutions through multiple conversion steps, while SAR ADCs are known for their efficiency, speed, and stability.
Characteristics:
- Highest resolution among basic A/D converter types (up to 32bits)
- Generally, the conversion speed is slower than successive approximation types.
- Poor response makes it unsuitable for applications that connect a multiplexer to the input for switching analog signals at high speeds.




