DRAM <Semiconductor Device Principles>
Memory Cell Structure
Consists of 1 Transistor and 1 Capacitor.
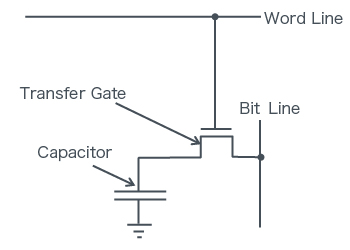
Data Write Method
In the Case of '1':
- Word Line potential is High
- Bit Line potential is High
- Word Line potential is Low
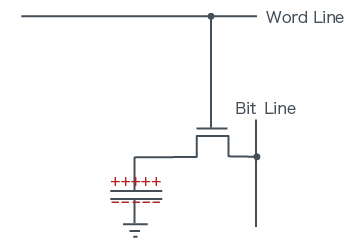
The state of '1'
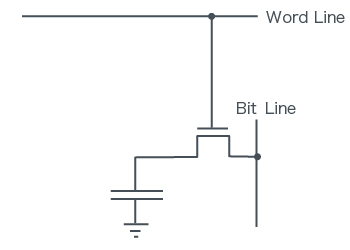
The state of '0'




