What is a capacitor?
With the ability to store electrical charge, block DC signals, and pass AC signals capacitors are play a pivotal role in electronic circuits.
As such they are used for backup (battery), decoupling (reduce noise), and coupling (remove DC bias voltage).
At type of passive component like resistors and inductors (coils), capacitors are used in everything from smartphones, wearables, and data centers to base stations, industrial equipment, and automotive systems.
Although the term capacitor is common in most parts of the world, in Japan it's often referred to as a condenser.
Structures and Features of Different Capacitors
Capacitors come in various types, but the basic structure consists of an insulator (dielectric) sandwiched between electrodes, capable of storing charge when a voltage is applied.
Actual products include single-layer, trench, multilayer, electrolytic, and wound types.
Capacitors can be differentiated by the following characteristics depending on the dielectric and electrode materials used.
Polarity, small/large size, thin/low-profile, operating temperature range, capacitance size, rated voltage range, high-frequency performance, capacitance stability, presence/absence of noise due to piezoelectric effects, etc.
Therefore, when selecting a capacitor, it is necessary to understand the characteristics of each type.
[Types and Characteristics of Different Capacitors】
*Scroll horizontally
| Silicon Capacitor | Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor | Tantalum Capacitor | Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacitor Appearance |  |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Electrode ① | 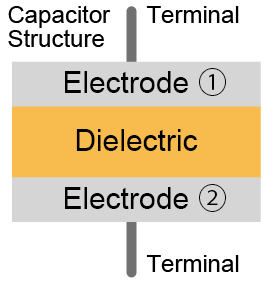 |
Doped silicon | Nickel | Tantalum (anode) |
Aluminum (anode) |
|||
| Dielectric | Silicon oxide or Silicon nitride |
Temperature compensating ceramic | High dielectric constant ceramic | Tantalum pentoxide | Aluminum oxide | |||
| Electrode ② | Doped silicon | Nickel | Manganese dioxide (cathode) |
Conductive polymer (cathode) |
Electrolyte (cathode) |
Conductive polymer (cathode) |
||
| Polarity | No | No | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Compact | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 〇 | 〇 | × | × | |
| Thin/Low Profile | ◎ | 〇 | 〇 | △ | △ | × | × | |
| Operating Temperature Range |
◎ | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | △ | 〇 | |
| Large Capacitance | △ | × | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | ◎ | ◎ | |
| High Rated Voltage | 〇 | ◎ | ◎ | 〇 | 〇 | ◎ | △ | |
| High Insulation Resistance (Low Leakage Current) |
◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 〇 | △ | 〇 | △ | |
| High Frequency Characteristics |
◎ | 〇 | 〇 | × | △ | × | △ | |
| Capacitance Stability | DC Bias |
◎ | ◎ | × | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ |
| Temperature | ◎ | ◎ | × | 〇 | 〇 | × | 〇 | |
| High Reliability | ◎ | 〇 | 〇 | × | △ | × | △ | |
| Noise (Ringing) | No | Yes | No | No | ||||
| Advantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
◎: Excellent 〇: Very Good △: Average ×: Poor
About Capacitance
Capacitance is a typical characteristic of a capacitor.
And is generally expressed by the following formula.
Capacitance=εr×ε0×S/d
(εr:Relative permittivity of the dielectric, ε0:Permittivity of a vacuum =8.9×10-12[F/m], S:Electrode surface area, d:Dielectric thickness)
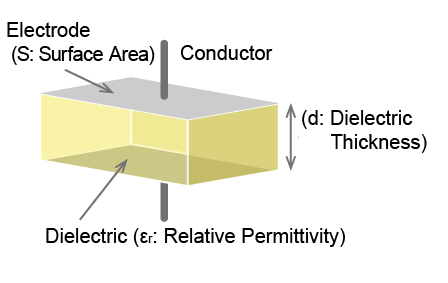
As the above equation shows, capacitance is proportional to the surface area of the electrode and dielectric constant of the dielectric and inversely proportional to the dielectric thickness.
Relative permittivity is an inherent value of the dielectric material used.
The unit of capacitance is F (farad), and in practice pF (picofarad), nF (nanofarad), uF (microfarad), mF (millifarad), etc. are commonly used.
( 10-12[F]=1pF, 10-9[F]=1nF, 10-6[F]=1[μF], 10-3[F]=1[mF] )




