Spanning from discrete to ICs and SiP, we offer strategies to enhance GaN Power efficiency.ROHM GaN Power Solutions

NEWS
- 2025-2-27 ROHM launches 650V GaN HEMT in a compact, high-heat dissipation TOLL package
- 2024-12-10 ROHM and TSMC Launch Strategic Gallium Nitride Technology Collaboration for Automotive Industry
- 2024-05-17 Stories of Manufacturing #6 Developing next-generation GaN power semiconductor devices GaN paves the way to carbon neutrality
- 2024-03-29 Industrial Equipment Pioneered by GaN Device & Driver IC【Satoru Oyama × ROHM Conversational Video】
- 2024-02-27 ROHM's EcoGaN™ has been adopted in the 45W Output USB-C Charger C4 Duo from Innergie, a brand of Delta
- 2023-11-08 ROHM’s New Ultra-High-Speed Gate Driver IC: Maximizing the Performance of GaN Devices
- 2023-08-31 ROHM’s New EcoGaN™ Power Stage ICs Contribute to Smaller Size and Lower Loss
What is GaN? What are GaN HEMTs?
GaN (gallium nitride) is a compound semiconductor that uses a compound of gallium and nitrogen; it is regarded as one promising material for next-generation power devices. Gallium nitride technology is known for its high efficiency and transformative impact on various applications in power electronics, photonics, LED technologies, RF infrastructure, and power ICs. GaN semiconductors are crucial in various technological applications such as 5G and 6G telecommunications, electric mobility, and energy-efficient lighting solutions. It should be noted that SiC is also a compound semiconductor, based on silicon and carbon. SiC serves as a substrate for growing GaN epi layers, particularly for applications in radio frequency and power devices. Silicon carbide is essential in developing high-performance semiconductor devices, including LEDs and power electronics, due to its superior thermal conductivity and stability in GaN applications. The main physical properties of Si, SiC, and GaN can be compared. Because GaN has a wider band gap and higher thermal conductivity than does Si, it is called a wide-band gap semiconductor. A wide-band gap semiconductor has the feature of a high dielectric breakdown electric field strength, and the same withstand voltage as Si can be achieved using thinner layers. HEMT is an acronym for High Electron Mobility Transistor; it refers to a field effect transistor in which a high-mobility two-dimensional electron gas induced at a semiconductor heterojunction functions as a channel. In general, HEMTs are fabricated in compound emiconductors, and in addition to GaN, they also use GaAs (gallium arsenide) and other materials.
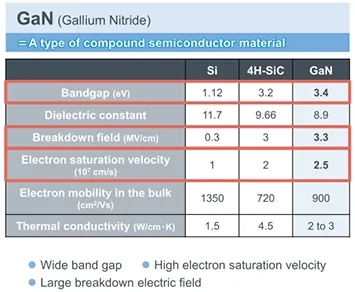
Definition and Physical Properties of GaN
Gallium nitride (GaN) is a binary III/V direct bandgap semiconductor material that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its unique properties. With a wide bandgap of 3.4 eV, GaN can sustain higher voltages and temperatures compared to traditional silicon MOSFETs, making it an ideal material for high-power transistors. This direct bandgap semiconductor is also known for its high thermal conductivity and mechanical stability, thanks to its Wurtzite crystal structure. These properties enable GaN devices to operate efficiently at high temperatures and resist mechanical stress, making them suitable for demanding applications in power electronics, such as high-frequency power conversion and high-efficiency power supplies. The combination of these physical properties allows GaN to deliver superior performance in a compact form factor, driving innovation in various industries.
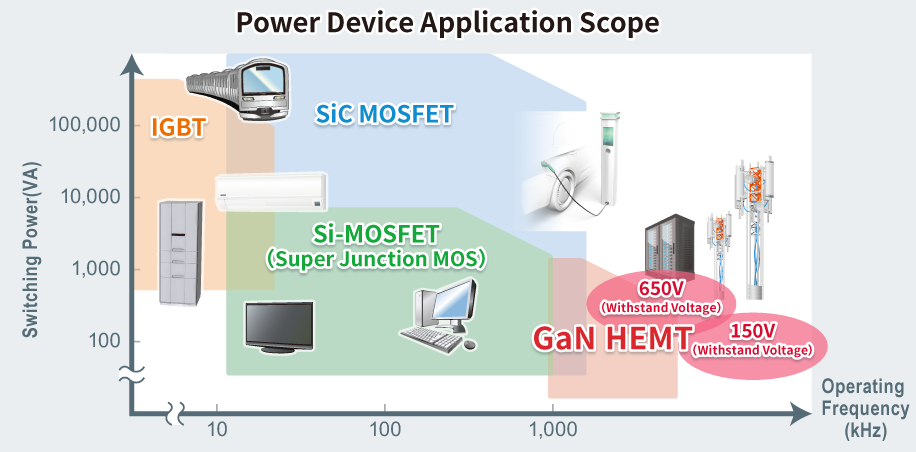
Application range of transistor power devices
Power devices have different power (VA) and operating frequency bands, depending on the materials and device. ROHM begins development of GaN device as a device to complement SiC and Si devices. GaN HEMT is expected as a device with extremely high frequency operation in the medium voltage range. GaN technology offers significant advantages over traditional silicon semiconductors, including higher speed and lower resistance, making GaN power transistors increasingly used in high-power and high-frequency devices, suitable for applications like power supplies in electronic equipment. Integrated circuits play a crucial role in increasing efficiency, shrinking size, and reducing the cost of power conversion systems.
●High Power
●High voltage (>650V)
●High frequency (20 to 200kHz)
- EV inverter, HV DC/DC, OBC
- Server primary power supply
- Solar/wind power
- Industrial power supply
- Railroad
SiC
●Middle power
●Middle voltage (100 to 650V)
●High frequency (More than 200kHz)
- Server power supply for data center
- Base station power supply
- Small AC adaptor(consumer)
- Automotive OBC, 48V DC/DC
GaN
Scaling GaN to Higher Power Levels
Enabling Higher Power Density
Scaling GaN to higher power levels is critical for enabling higher power density in power electronics systems. By increasing the power handling capability of GaN devices, designers can develop more compact and efficient power systems that meet the demands of emerging applications, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and data centers. GaN power transistors and GaN power ICs are being developed to operate at higher power levels, enabling the development of more efficient and compact power systems. The use of GaN technology innovations, such as GaN power transistors and GaN power ICs, is expected to play a key role in the development of next-generation power electronics systems. These advancements will drive the future of high-efficiency, high-frequency power conversion, making GaN a cornerstone of modern power electronics.
Benefits and Challenges of GaN Power Solutions
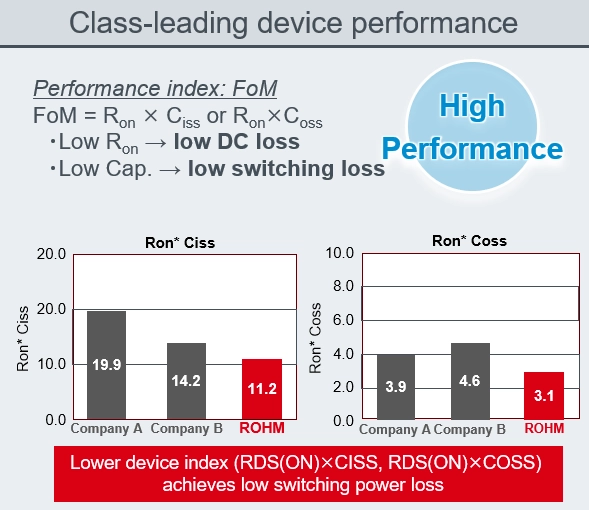
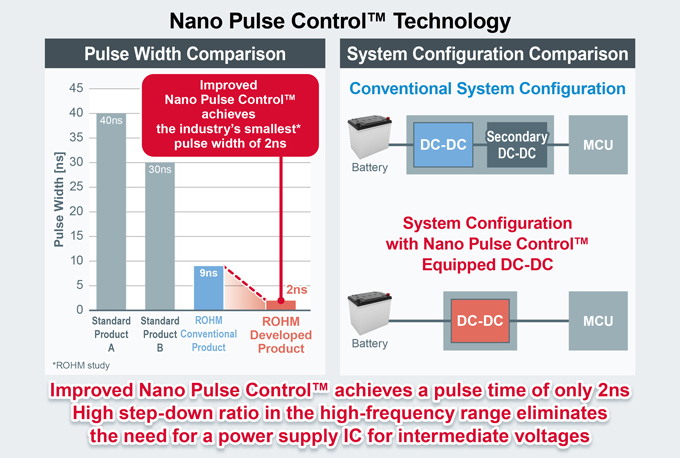
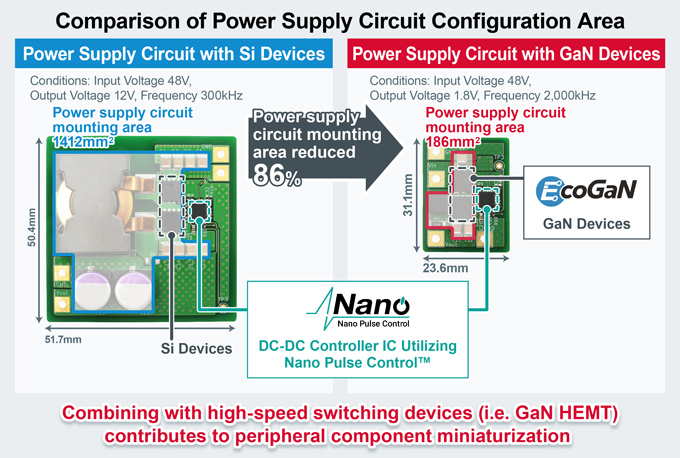
GaN offers several compelling advantages over traditional silicon-based power electronics. One of the primary benefits is the ability to achieve higher power density, which enables the development of smaller, more efficient power converters and motor drives. GaN power transistors are known for their faster switching speeds, lower on-resistance, and higher thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-frequency and high-power applications. GaN HEMTs, in particular, play a crucial role in achieving these benefits by operating at higher temperatures and voltages compared to traditional silicon-based transistors. These characteristics allow GaN devices to operate at higher temperatures, reducing the need for extensive cooling systems and increasing overall system reliability. Additionally, the high efficiency of GaN power translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs, making them a preferred choice for applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial power supplies and renewable energy systems. The greatest advantage of GaN HEMTs is their ability to operate at high frequencies. They can function at frequencies above 3MHz, not just a few hundred kHz. So, why is there a push towards higher frequencies in power supplies? This is because the largest components in power supplies are passive components, namely capacitors and inductors (coils). By increasing the frequency, these components can be miniaturized. However, there are two challenges to high-frequency operation at present. Oneis the need for Power Controller ICs operating at high frequencies up to 3 MHz. The other challenge concerns magnetic components such as inductors and coils. Magnetic components suitable for high-frequency operation have not yet been commercialized, and there is no clear solution in sight. Current inductors and capacitors have issues with high-frequency characteristics, and they do not operate ideally at frequencies above 1MHz. Therefore, it is difficult to operate GaN HEMTs in the MHz range at present, and they are only barely usable. In other words, the performance of GaN HEMTs cannot be fully utilized without solving these challenges. However, by increasing the voltage resistance, it is possible to bring out the advantages of GaN HEMTs without raising the frequency so much. This is why 650V voltage-resistant products are adopted in AC adapters and are widely used. To leverage the strengths of GaN HEMTs, it is necessary to design power circuits that are most suitable for high-frequency driving using dedicated gate driver ICs. This involves selecting circuit topologies, optimizing transformers (magnetic components), and implementing noise and thermal countermeasures. When GaN HEMTs are driven at high frequencies, ringing occurs when high-speed commands (signals) are input to the gate electrode. Thus, when trying to drive in the MHz range for applications such as AC adapters and USB chargers, noise and thermal design become challenging. High-frequency operation encounters issues where the parasitic inductance of the board on which GaN HEMTs are mounted interferes with their operation, preventing them from functioning properly. Designing in the same way as Si power MOSFETs leads to various troubles.
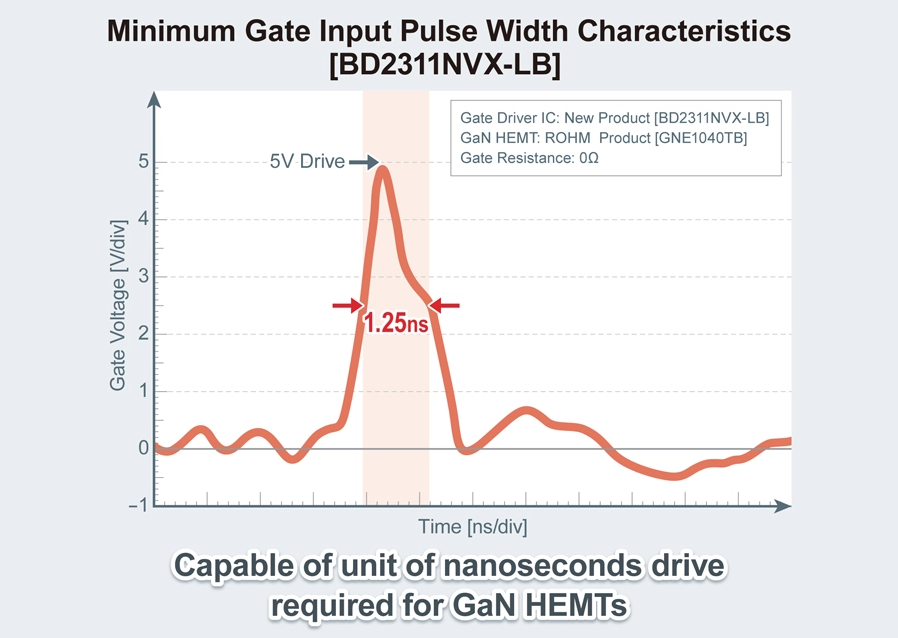
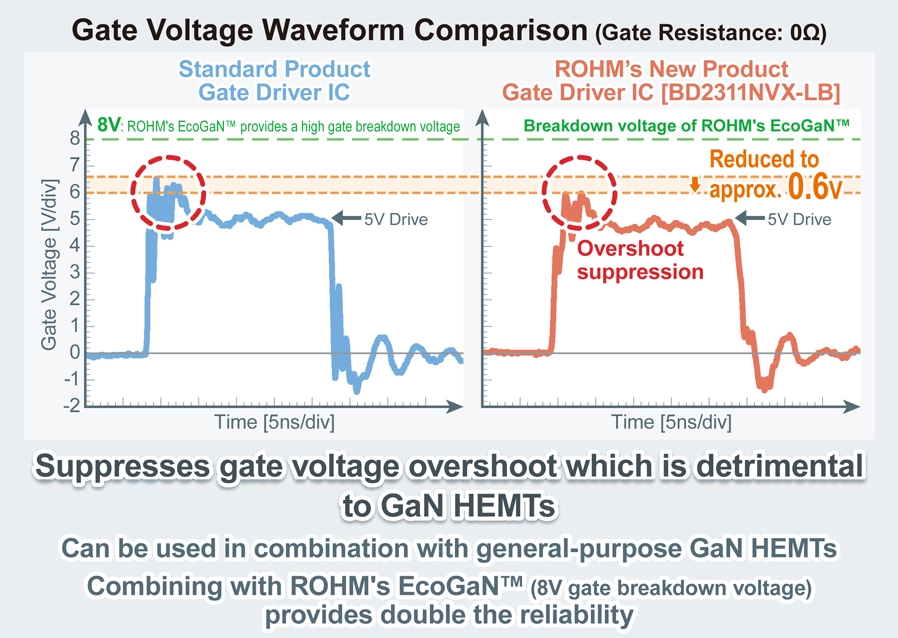
- Answer to the Low Rated Values of the Gate-Source Voltage VGS (GaN HEMT)
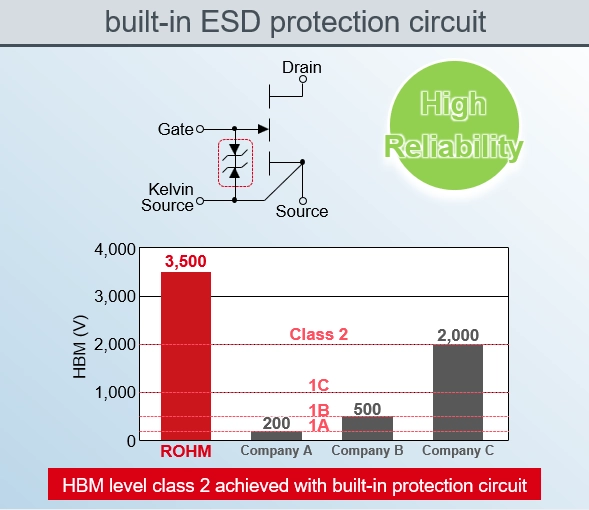
- Standard GaN HEMTs, which have a rated voltage of 200 V or less, typically feature a gate-source voltage (VGS) rating of 6 V, with a gate driving voltage of 5 V due to their structural design. This results in a narrow gate driving voltage margin of just 1 V. The rated voltage is a critical threshold that must not be surpassed; exceeding it can lead to operational issues, degradation, and in the worst case, device failure. Therefore, precise control is essential to ensure the gate driving voltage remains within the VGS rating. This requirement has posed a significant challenge to the widespread adoption of GaN HEMTs.
- Answer to the Difficulty in Handling the Packages (GaN HEMT)
- Many GaN HEMTs use packages such as BGA (Ball Grid Array), which are not familiar to general circuit designers, making the mounting and inspection processes challenging. To address these difficulties, it is recommended to adopt GaN HEMTs with highly versatile packages like DFN5060. The DFN5060 package offers high reliability and excellent board mounting performance, supports large currents, and boasts superior heat dissipation. Additionally, copper clip bonding package technology is effective, reducing parasitic inductance values by 55% compared to conventional packages, resulting in superior switching characteristics in high-frequency operation.
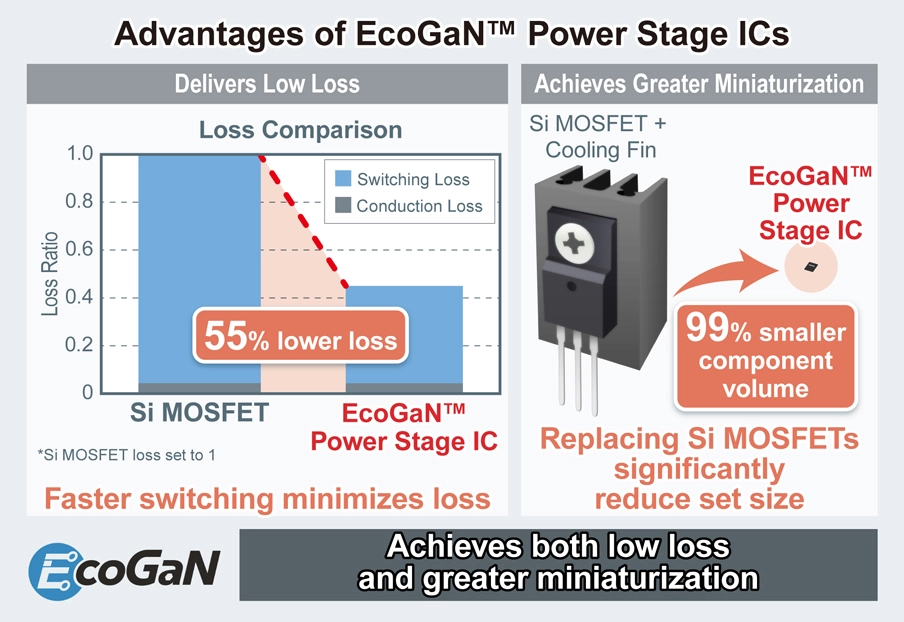
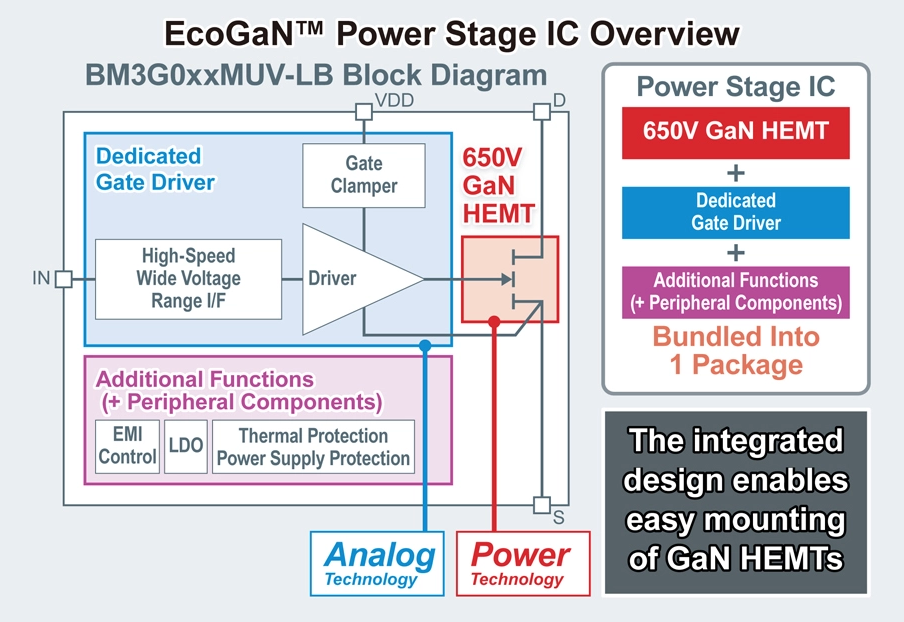
- Answer to the Complexity of Addressing Noise Countermeasures and Thermal Design (GaN SiP)
- Although GaN HEMTs are anticipated to play a major role in reducing size and enhancing power conversion efficiency, their gate handling complexity, in contrast to silicon MOSFETs, necessitates the use of a specialized gate driver.. To address this, SiP, or power stage ICs that integrate GaN HEMTs and gate drivers into a single package, leveraging core power and analog technologies, would be a convenient solution for power circuit engineers by greatly simplifying the mounting process.
ROHM Current GaN Product Lineup (EcoGaN™)
|DC-DC Controller for GaN
|Gate Driver ICs for GaN
ROHM Upcoming GaN Products (Eco GaN™)
As to [sample available] and [sample MM/YY], you can download tentative datasheets by clicking product names below. Please note that specifications are subject to change without notices as those documents are still under development. When you click to view the materials, you will be prompted to log in to MyROHM. By registering with MyROHM, you will be able to view and download such materials.
Upcoming Discretes
- 【TOLL Package】
- GNP2025TD-Z

- GNP2050TD-Z

- 【TOLT Package】
- GNP3018TF-Z

- GNP3028TF-Z

- GNP3040TF-Z

Upcoming Drivers
- 【Single GDIC】
- BD2312AGWL-LB

- BD2311ANVX-LB

- BD2311ANVX-C

- 【Single GDIC with LDO】
- BD3GD**NVX-LB

- 【Half bridge Driver】
- BD4HB00FV-LB

Upcoming Power Stages
- 【DFN Package】
- BM3G204TCC-LBZ

- BM3G205TCC-LBZ

- BM3G207TCC-LBZ

- BM3G212TCC-LBZ

- 【TOLL Package】
- BM3G201TD-LBZ

- BM3G202TD-LBZ

- BM3G204TD-LBZ

- BM3G205TD-LBZ

- BM3G207TD-LBZ

- BM3G212TD-LBZ

- 【TOLT Package】
- BM3G201TF-LBZ

- BM3G202TF-LBZ

- 【Half bridge】
- BM4G005MUV-LB

Upcoming Power Stages
- 【QR Flyback】
- BM3GQ1A2MUV-LBZ

- BM3GQ1A3MUV-LBZ

- 【BCM PFC】
- BM3GF01MUV-LBZ

- BM3GF02MUV-LBZ

Upcoming Controller
- 【TP-PFC】
- BM85060FV

- 【LLC】
- BM85080FV-LB

- 【AHB】
- BM1AH001FV-LB

GaN Reference Designs for Enhanced Application Performance
REFLD002 Laser Driver Reference Design with GaN HEMT for High-Resolution LiDAR
GaN improves LiDAR distance resolution due to its Narrow and Sharp Pulse.
The range of uses for LiDAR sensors is expanding to include not only autonomous driving, but also applications in the industrial and infrastructure fields. GaN transistors, known for their faster switching speed and higher thermal conductivity, play a crucial role in enhancing these applications.
LiDAR sensors are required to have longer sensing distance and higher resolution, and in addition to improving the characteristics of the laser diode, it is necessary to drive the laser diode at higher speeds and power. ROHM offers a lineup of 905nm high power narrow emission width laser diodes. (RLD90QZWx Series) Reference designs are available that includes EcoGAN™, a next-generation device capable of high-speed drive, along with a high-speed gate driver for GaN HEMTs that contribute to improved LiDAR sensor characteristics (distance and resolution) .

REFACDC047 With GaN HEMT, Power Factor Correction, 240W 400V BM3G007MUV Reference Board
Power supply for industrial equipment~Power Factor Correction by using this GaN Power Stage, we achieved a maximum efficiency of 97.8%.
The BM3G007MUV-EVK-002 reference board outputs 400 V voltage from the input of 90 Vac to 264 Vac. The output current supplies up to 0.6 A.BM3G007MUV has a built-in GaN HEMT (650V 70 mΩ), driver and protection circuit. By using this GaN Power Stage, we achieved a maximum efficiency of 97.8%.
Buck Converters,Boost Converters,Half Bridges,and Isolated... Our revolutional GaN reference designs are coming soon. Contact Us
What is EcoGaN™?
ROHM continues to improve device performance through its EcoGaN™ lineup of GaN devices that contributes to greater energy application savings and miniaturization. While developing ROHM products, we will also promote joint development through strategic partnerships to contribute to solving social issues by making applications more efficient and compact.
- * EcoGaN™ is a trademark or registered trademark of ROHM Co., Ltd.

Application samples using Gallium Nitride
~ ROHM’s GaN power solutions advance diverse applications ~
AC Adaptor

Reduction of Device Size
Shorter Charging
On Board Charger(OBC)

More Efficient Power Conversion
Shorter Charging
Data-Center

CO2 Cut
Power Reduction
Industrial Robot
Higher Power Density
Lower System Cost
Related Contents
-
Stories of Manufacturing

GaN power semiconductor device
-
VIDEO

Industrial Equipment Pioneered by GaN Device & Driver IC 【Satoru Oyama×ROHM Conversational Video】
-
Adoption・Collaboration Examples

ROHM's EcoGaN™ has been adopted in the 45W Output
USB-C Charger C4 Duo from Innergie, a brand of Delta
- * EcoGaN™ is a trademark or registered trademark of ROHM Co., Ltd.