How can AI and IoT solutions be used to address challenges in the manufacturing industry?
11/20/2023
Digital Transformation (DX) in the manufacturing industry is revolutionizing production processes. Among these, smart factories in particular are garnering increased attention.
Although the general image of a smart factory is a futuristic place that combines collaborative robots and AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) together with AI technology and large amounts of analytical data to automate operations and save labor, in reality, a smart factory can be achieved by simply incorporating IoT technology utilizing sensors into existing operational systems.
Smart factories not only improve productivity, quality, and safety while reducing costs and environmental impact, they also enable real-time failure prediction, reducing the risk of serious repairs, replacements, and line stoppages through AI chips installed on individual equipment and devices.
ROHM offers machine health solutions equipped with on-device learning AI chips capable of standalone operation along with a lineup of machine health-related products such as sensors and wireless communication ICs.
Now, let’s talk about the hidden potential of smart factories and the benefits they bring to companies and factories.
Smart Factories
Smart Factories
A smart factory is a manufacturing system that integrates physical processes with advanced digital solutions. Using wireless communication to collect internal and external manufacturing-related data and leveraging analog-digital fusion techniques enables seamless coordination of all processes from product design and manufacturing to inspection and distribution, significantly improving efficiency. This is where technologies such as automation, data analysis, IoT, and AI are incorporated to solve factory issues.
Benefits and Future Possibilities of Smart Factories
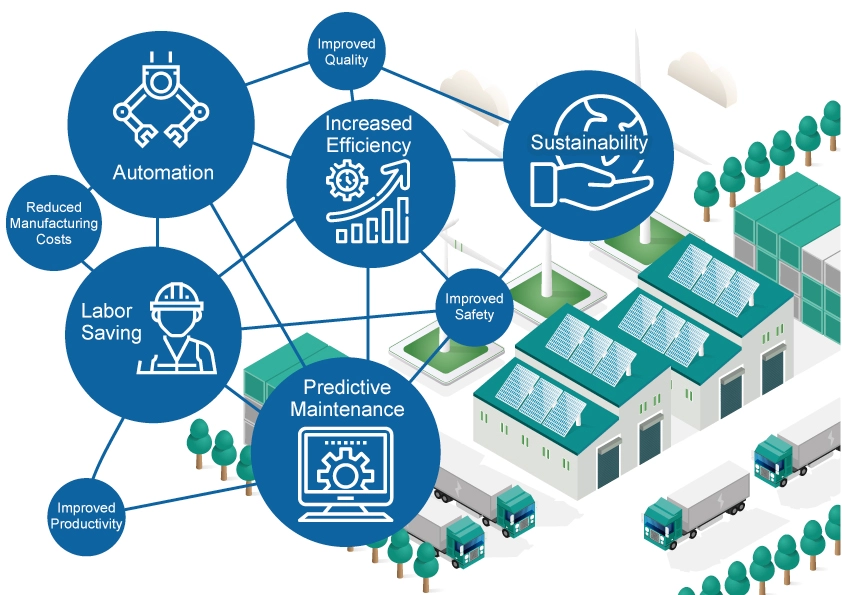
Smart factories bring a number of benefits to manufacturers, including increased productivity and safety, reduced manufacturing costs, and improved quality control. Real-time data analysis and remote operations allow for a more efficient and sustainable production system. The labor shortage, which is currently a major issue in the manufacturing industry, can be solved through automation and labor savings in smart factories.
Technological Elements in Smart Factories
The Role of IoT in Smart Factories
A central element in smart factories is IoT technology that combines advanced sensing with wireless communication.
Data collected through sensors facilitates production management in the manufacturing industry while significantly improving productivity through effective use of IoT and wireless communication.
Sensor-connected IoT devices allow for real-time monitoring of the entire production line and make precise adjustments as needed. This improves productivity and quality by reducing errors.
Smart Factories are Not Just About Robots
Smart factories aren’t just about state-of-the-art robots and AMRs. Combining various sensors and wireless communication technologies with existing manufacturing equipment makes it possible to enjoy the benefits of a smart factory, such as increased productivity and safety, greater labor savings, reduced manufacturing costs, and improved quality control.
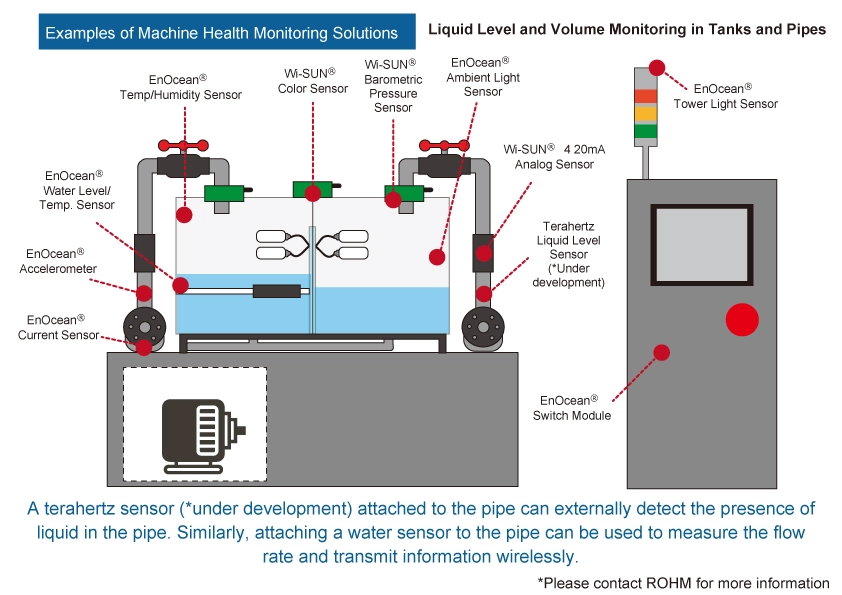
Accelerometers
Accelerometers can detect tilt, shock, and vibration. ROHM accelerometers offer 3 key features ideal for industrial applications: a high sensing range (up to 64g), wide temperature range (-40°C to 105°C), and compact form factor (2mm x 2mm). Compatibility with equivalent general-purpose products enables use over a wide frequency range required by industrial applications.
Color Sensors
These types of sensors detect abnormalities by automatically identifying and classifying the color of products, materials, liquids, and the like. For example, a factory can use color sensors to determine the color of the liquid in a rotary pump or turbidity of the water in a water tank.
Current Sensor
Current sensors contribute to the safety and high efficiency of power management and control systems by measuring motor current to enable efficient control and monitor for overcurrents, etc.
Ambient Light Sensors
These sensors measure the intensity and brightness of light to optimize the performance of lighting equipment. Monitoring brightness and adjusting light intensity makes it possible to improve energy efficiency required by smart factories.
ROHM can propose solutions combining these sensors with wireless communication technologies such as Wi-SUN® and battery-free EnOcean®that contribute to achieving smart factories.
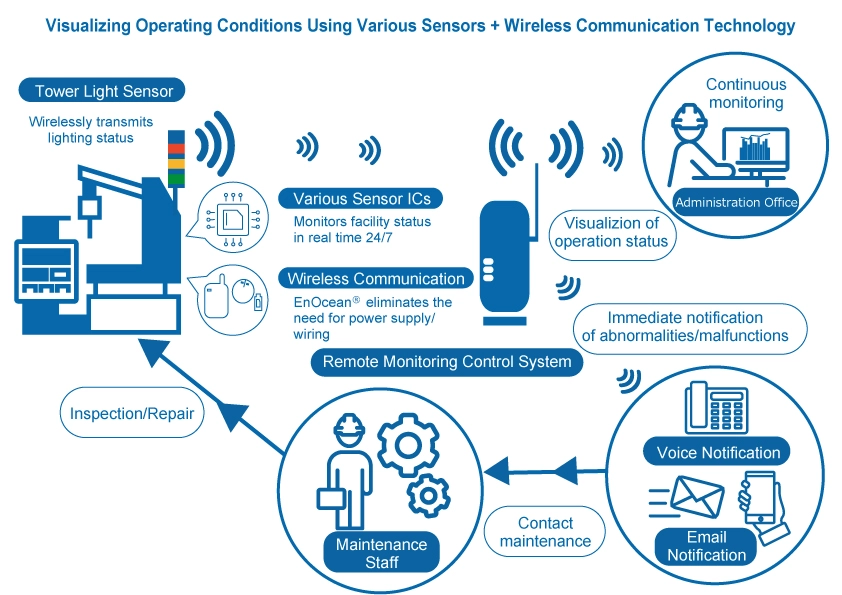
Collecting, Analyzing, and Using Data
Smart factories rely on large amounts of data collected by IoT devices to optimize production processes. This data is used to improve quality control, increase production efficiency, and perform predictive maintenance through AI and advanced data analysis technologies. Employing a data-driven approach can help manufacturers deliver transformative value to gain a competitive edge.
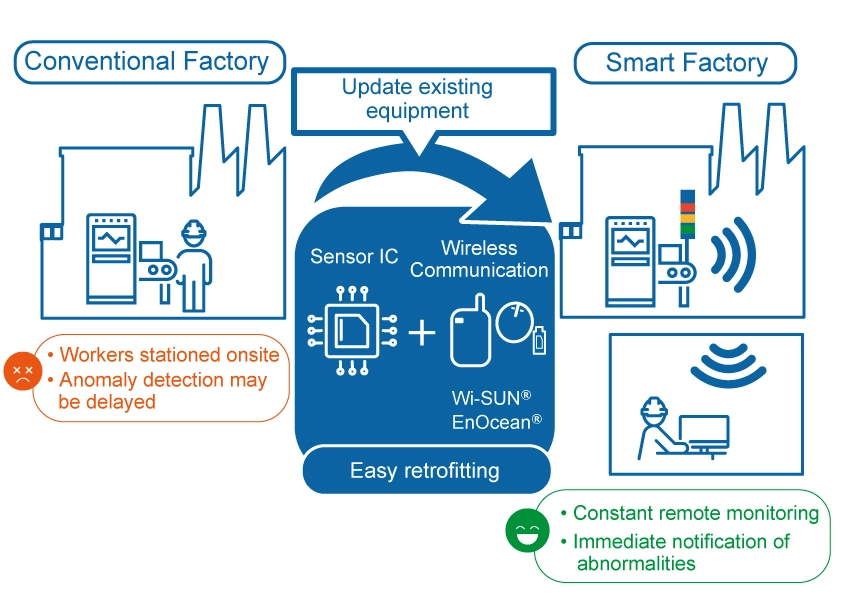
However, traditional systems require numerous cables, power supplies, computers, and storage systems for sensors to acquire and transmit data. This is both costly and time-consuming, raising the hurdle for implementation.
To address this issue, ROHM developed a sensor node that is compact, easy to mount, and reduces installation costs and time by combining EnOcean®'s battery-free technology with low-power Wi-SUN® to provide stable communication even inside factories. We propose wireless solutions that can be easily installed in existing equipment to enable machine health monitoring.
*EnOcean® is a registered trademark of EnOcean GmbH.
*Wi-SUN® is a registered trademark of Wi-SUN Alliance.
Challenges and Measures for Smart Factories
Smart factories use advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and data analytics to increase productivity, improve quality control, and reduce costs.
At the same time, however, they are expected to face a number of challenges related to implementation and operation, including the following.
Lack of Skills and Knowledge
One of the main challenges of smart factories is the lack of human resources capable of understanding and properly operating new technologies.
There are 3 main ways to solve this.
The first is to strengthen employee education and training. The second is to hire skilled external personnel. And the third is to compensate for the lack of skills and knowledge by successfully implementing and utilizing technologies such as IoT and AI.
For example, making the functions of existing systems smarter through IoT technology using sensors, wireless communication, and AI can lead to increased automation and labor savings without the need to introduce new systems, reducing the burden on employees and engineers.
Security Risks
As more IoT devices are deployed and data shared, so too are cybersecurity risks. As such, network countermeasures must include stronger security policies and installing specialized security systems.
Challenges for Data Management and Analysis
In general, smart factories generate a large amount of data that requires proper data management and analysis for effective utilization. This can be achieved by implementing advanced analytical tools and AI-based data analysis.
Implementation Costs
Management may hesitate to introduce smart factories due to the large initial investment and high cost of maintenance. However, while the introduction of industrial robots and automated conveyor systems requires careful planning and appropriate ROI calculations, updating existing production systems can help achieve a smart factory while minimizing implementation costs.
Regulatory and Standardization Issues
With the introduction of smart factories, various regulatory and standardization issues will invariably emerge related to data privacy/security and equipment compatibility. To address these, proper governance and an understanding of the relevant laws and regulations is necessary.
‘Unconnected’ Smart Factories
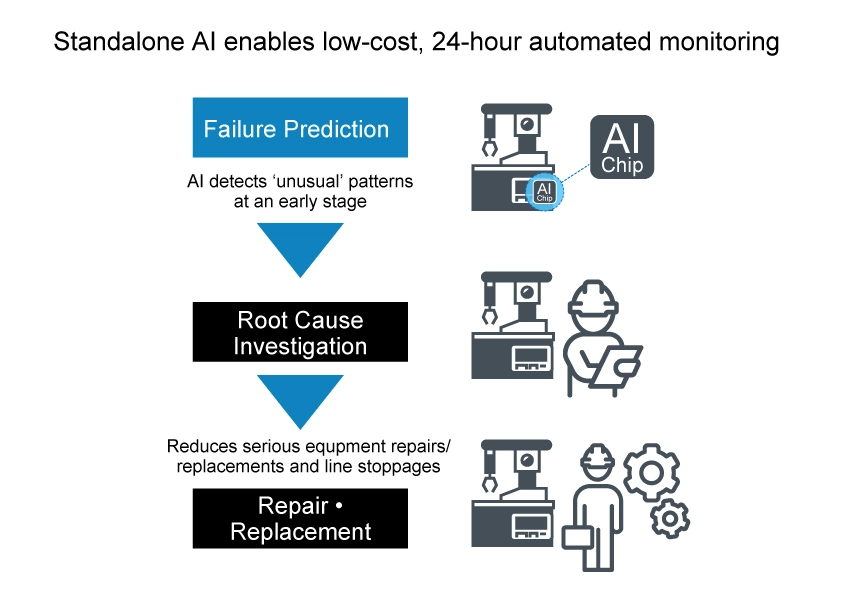
On the other hand, there are increasing calls for smart factories that are deliberately not connected. For example, ROHM is developing ‘Solist-AI™’, an AI solution that enables on-device learning at the endpoints (unlike conventional AI systems that carry out all learning and inference in the cloud) by embedding standalone AI chips directly into every device and sensor.
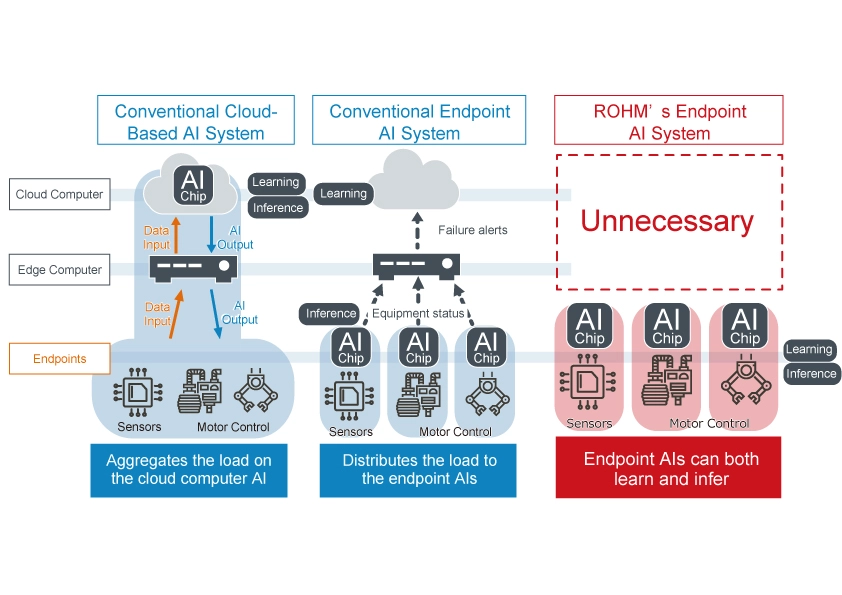
The major advantages of endpoint AI are reduced network load, extremely short response times, and significantly lower power consumption. However, with traditional endpoint AI it is difficult to learn on the device, so reliance on a host system is necessary via a cloud server, entailing a significant amount of manpower and costs.
ROHM’s Solist-AI™ is a standalone AI Solution capable of onsite learning that allows the AI to learn (analyze) and infer the normal state of each device in a variety of installation environments Re-learning can also be easily performed for each installed device. This eliminates the reliance on cloud networks and servers, contributing to reduced man-hours, costs, and power consumption. We are currently developing the ML63Q2500 Group of AI chips equipped with an ARM Cortex M0+ and on-device learning AI accelerator (samples in 2024 with mass production planned for 2025).
*Solist-AI™ is a trademark or registered trademark of ROHM Co., Ltd.
Examples of Solution Applications in Smart Factories
Optimizing Operations with IoT and AI
1. Deploy IoT Devices: Get real-time data from the field
2. AI Analysis: AI analyzes acquired data to understand patterns
3. Predictive Modeling: Predict anomalies and potential problems based on analysis results
4. Automation: Automate actions based on forecast results to optimize operations.
ROHM’s industrial solutions improve manufacturing efficiency and contribute to proper quality control by updating existing production systems with cutting-edge technologies.
The Impact of Smart Factories and the Vision for the Future
Future Predictions and Their Far-Reaching Implications
Smart factories have the power to transform the future of companies and factories. Not only do they significantly increase productivity and efficiency, they also provide supply chain visibility, create new business models, and potentially trigger a paradigm shift in the entire industry. This is because smart factories integrate digital technology with physical manufacturing processes that enable real-time data analysis and forecasting.
Creating New Trends in Sustainability, Predictive Maintenance, and More
The evolution of smart factories is creating new trends. One is the pursuit of sustainability. Smart factories help reduce environmental impact by increasing energy efficiency and minimizing waste in the production process. Furthermore, by making effective use of data, it becomes possible to predict equipment failures and optimize maintenance activities through predictive maintenance. These key elements allow companies to achieve a sustainable and efficient future.
Summary
Smart factories are poised to revolutionize the future of corporate manufacturing. This opens up the possibility of DX manufacturing, improving factory productivity and quality, visualizing the supply chain, and creating new business models through cutting-edge technologies such as IoT, AI and data analysis. Smart factories are also driving new trends in the manufacturing industry, including the pursuit of sustainability and predictive maintenance. These key elements allow companies and factories to achieve a sustainable and efficient future. ROHM contributes to solving problems in the manufacturing industry by making factories smarter through IoT (sensors and wireless communication) and AI solutions that can be retrofitted to existing equipment and systems.
At the same time, as achieving a smart factory involves changing the equipment in the factory itself, ROHM contributes to making equipment more efficient and compact by taking advantage of its strengths in power devices and analog ICs. In the next article we will introduce these products for the energy field, which like factory automation for industrial equipment are expected to see increased demand.
Product Information and Related Links
Wireless Communication Modules
Solving Challenges in the Logistics Industry with LiDAR
