Wireless Communication
<Short-Range Wireless Communication>
Short-Range Wireless Communication Standards
Although there is no detailed classification for short-range wireless communication, it generally refers to communication distances on the level of WPAN and WLAN.
Recently, there has been a shift to wide range wireless communications such as FAN (Field Area Network) utilizing multi-hop technology.
Multi-hop
Compared to single-hop where nodes communicate directly with each other, multi-hop enables communication over a wider range by transmitting data using multiple nodes.
| Relay Function | Single-Hop | Multi-Hop |
 |
Features of Short-Range Wireless Communication
Here we compare features of tipical short-range wireless communication protocols.
Features
The graph below shows the short-range wireless standards, with the horizontal and vertical axes indicating the communication distance and data rate (speed), respectively.
The further to the right and up the faster the speed and greater the communication distance.
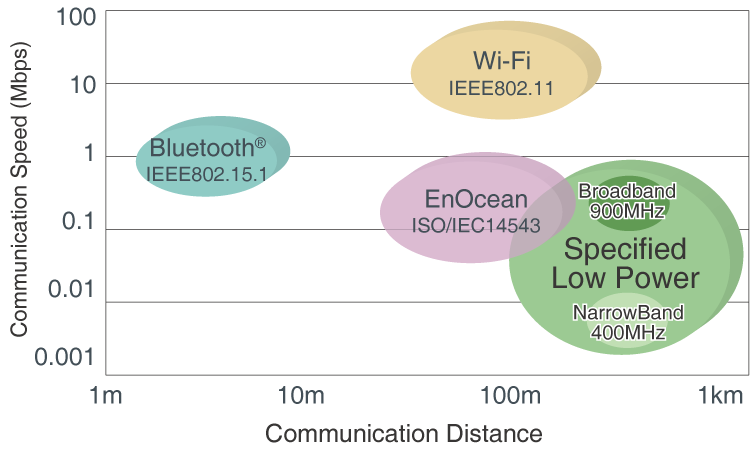
| Bluetooth® | Wi-Fi | EnOcean | Specified Low Power | |||
| Broadband | Narrow Band Wi-SUN | |||||
| Frequency Band | 2.4GHz | 2.4GHz | 5.0GHz | 315/868/905/920MHz | 426/429MHz | 900MHz |
| Communication Distance | ~10m | Several hundred m | ~200m | ~1km | ||
| Transmission Speed | 1Mbps~ | 11Mbps~ | 125kbps | ~9600bps | 50kbps~ | |
| Available Channels | 79 | 13 | 19 | - | 46 | |
| Transmission Time Limit | No | No | Yes | Yes | ||
| Modulation Method | FSK/PSK | DSSS/OFDM | ASK/FSK | FSK | ||
Please refer to the next page for an explanation of modulation methods
Bluetooth®
Examples of WPAN include Bluetooth®. It use the 2.4GHz band.
For applications that continuously transmit data (i.e. sensor information from a gaming controller or music from a mobile device to a speaker) the fast communication speed of Bluetooth® is particularly effective.
EnOcean
EnOcean is a system for transmitting data wirelessly that requires no power supply or maintenance, and instead uses energy harvesting technology to generate the small amount of energy needed from the environment (i.e. light, temperature difference).
The frequency varies depending on region. In Japan this is classified as specified low power wireless using the 315MHz and 928MHz frequencies. In the US 315MHz and 902MHz are employed while the EU adopts 868MHz.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi utilizes the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands and features fast communication speeds.
This, combined with a communication distance of about 100m, make it the preferred method for implementing a wireless network for connecting to the internet in the home.
Wi-SUN
This standard has been attracting increased attention since its adoption by power companies in Japan for smart meter communication.
Japan uses the 920MHz band referred to as specified low power, which is characterized by slower communication speeds than Wi-Fi but features longer communication distance, lower power consumption, simpler connection, and greater performance against obstacles.
A broad lineup of wireless communication modules are offered that utilize a variety of technologies. ROHM Sub-GHz specified wireless communication modules are capable of transmitting and receiving with very low power. Wi-SUN compatible modules are also offered.