wireless_what1
Wireless<What is wireless?>
What is wireless? This refers to communication using radio waves, light, or other methods without wires.
Radio waves are capable of covering a wide area, and as a result are adopted in a variety of applications, including radio and TV broadcasting.
In recent years, with the advancement of encryption technology, usage has spread from public use to individual communication represented by mobile phones and wireless LAN.
Another wireless method, light (visible, infrared), is characterized by strong directivity, making it ideal for remote control and similar applications.
Here, we will focus on tipical short-range wireless methods.
Wireless Communication Standards
First, wireless communication is broadly classified according to communication distance.
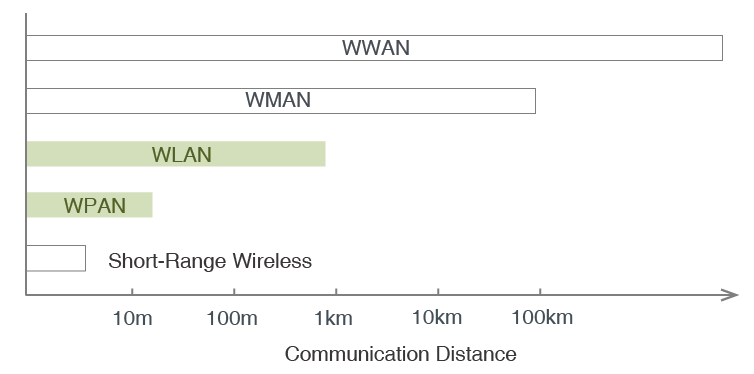
Short-Range Wireless
An example of a short-range wireless network is NFC (Near Field Communication).
munication is easily achieved by simply holding a non-contact IC card (i.e. Felica, MIFARE) over a reader.
WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network)
This method features a communication distance of several cm to several m.
Standards in this class include IrDA and Bluetooth® .
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
Achieved by wirelessly interconnecting computers in rooms and buildings (e.g. Wi-fi).
WMAN (Wireless Metroporitan Area Network)
Primarily used for communicating large amounts of data at high speeds.
The area corresponding to each base station is relatively small, with communication limited to that area.
WWAN (Wireless Wide Area Network)
Connects remote networks using data lines.
Allows communication between devices and to the internet through base stations utilizing mobile cellular and other technologies.
electronics_tips_menu