memory_what1
What is Semiconductor Memory?
Semiconductor memory is a type of semiconductor device tasked with storing data. There are two electronic data storage mediums that we can utilize, magnetic or optical.
Magnetic storage:
- Stores data in magnetic form.
- Affected by magnetic fields.
- Has high storage capacity.
- Doesn't use a laser to read/write data.
- Magnetic storage devices are; Hard disk , Floppy disk, Magnetic tape etc.
Optical storage:
- Stores data optically, uses laser to read/write.
- Not affected by magnetic fields.
- Has less storage than a hard disk.
- Data accessing is high, compared to a floppy disc.
- Optical storage devices are; CD-ROM,CD-R, CD-RW, DVD etc.
There is also volatile memory. This is memory that loses its data once power is cut off, while non-volatile memory retains data even without power.
Semiconductor Memory Types
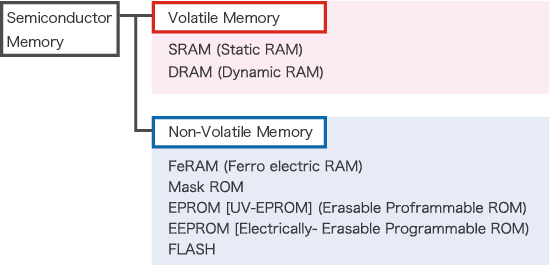
* RAM (Random Access Memory) : Enables Read/Write of stored contents
* ROM (Read Only Memory) : Allows only Read operation
Characteristics of Various Types of Memory
| Parameter | RAM | ROM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volatility | Non Volatility | ||||||
| SRAM | DRAM | FeRAM | Mask ROM | EPROM | EEPROM | FLASH | |
| Data Storage Method | Voltage Bias | Voltage Bias + Refresh |
Unnecessary | ||||
| No. of Read Operations | ∞ | ∞ | 10 billion to 1 trillion times |
∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ |
| No. of Rewrites | ∞ | ∞ | 0 times | 100 times | 100,000 to 1 million times | 10,000 to 100,000 times | |
| Write on Substrate | Possible | Possible | Possible | × | × | Possible | Possible |
| Read Time | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Write Time | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | - | △ | △ | △ |
| Bit Cost | △ | ○ | △ | ◎ | △ | △ | ◎ |
| Larger Capacity | ○ | ◎ | △ | ◎ | △ | △ | ◎ |
| Memory Cell | 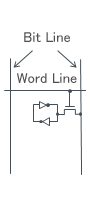
Stored in a flip flop circuit |
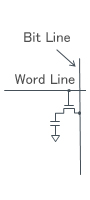
Maintains charge in the capacitor |
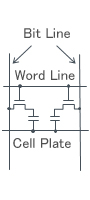
Polarization of the ferroelectric material |

Ions implanted in a transistor |
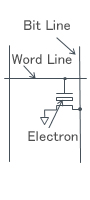
Maintains charge in the floating gate |
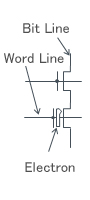
Maintains charge in the floating gate |
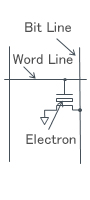
Maintains charge in the floating gate |
electronics_tips_menu